
In this post Allan Figueroa, software developer in the UK Data Service Census and International Macrodata team based in Jisc, discusses a new extension that has been implemented into the Census bulk download tool, CKAN.
What is CKAN?
CKAN (Comprehensive Knowledge Archive Network) is an open-source data portal used for storage and distribution of open data. The UK Data Service uses this portal to provide data for England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales from the 1971, 1981, 1991, 2001, 2011 and 2021/2022 UK censuses. The data can be found in several formats such as docx, pdf, xlsx and more. Information about CKAN can be found in this previous blog post and you can access the tool here.
One of our goals in the team is to not only make data available as soon as possible on our platforms, but also to improve the user experience. This could be in the area of accessibility, in adding functionality to the platforms or any other area.
In the past couple of months, we have been looking to implement the Data Catalog Vocabulary (DCAT) on the CKAN platform.
What is DCAT?
DCAT is the solution we decided to implement to allow us to make the data available in CKAN more discoverable and visible. It is a standard way to publish machine-readable metadata about a dataset and it provides Resource Description Framework classes and properties to allow datasets and data services to be described and included in a catalog. The use of a standard model and vocabulary facilitates the consumption and aggregation of metadata from multiple catalogs, which can:
- Increase the discoverability of datasets and data services.
- Allow federated search for datasets across catalogs in multiple sites.
The DCAT extension provides tools and guidance to allow publishers to publish and share DCAT based metadata easily. It facilitates the access to metadata through specific URLs where the information is provided in different formats (such as xml, turtle, Notation3 or JSON-LD). Information about these formats can be found here.
It also provides an easier way to create new datasets from other platforms that expose their metadata the same way as DCAT. JSON objects that are based on DCAT terms are also possible to import.
Thanks to one of the features included in DCAT, called “structured data”, it is also possible to provide richer metadata for search engines crawling the CKAN platform (such as Google Dataset Search). This improves discoverability of the datasets published, making it easier to find for the people who could need this information.
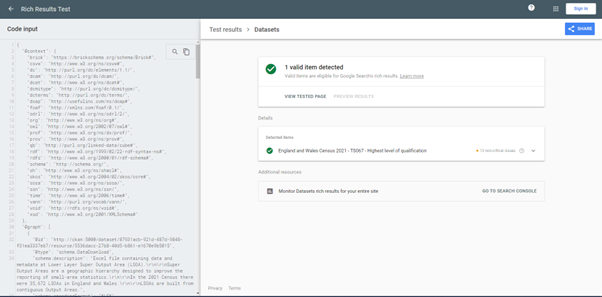
Rich Result Test output with one of the datasets available in CKAN.
Along with the DCAT installation, a new feature to make all this information more accessible for everyone has been included as well. We now provide a new section in each dataset page called “Machine-readable data”, where users can find the different formats the dataset information is exposed in CKAN. In the section title, users can also find a pop-up when clicking on the name of the section, that explains what “Machine-readable data” is and what are the formats available. Finally, there is a link to DCAT documentation with more technical information about the extension.
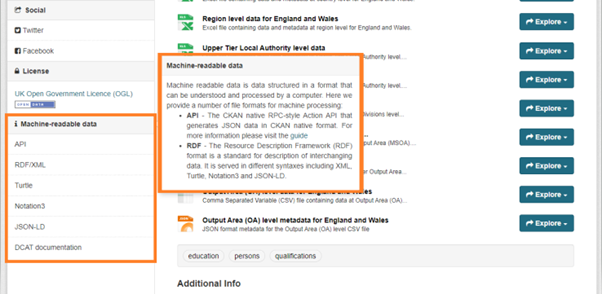
Machine-readable data side section and informative “pop-up” available in the dataset page in CKAN.
What next?
Currently, the main focus of our team is the release of ‘Census 2021’ data for England, Wales and Northern Ireland as it is made available by the National Statistical Institutes. At the same time, we are working on the implementation of a solution to improve the resources display for a more “user-controllable” way. We also aim to improve the handling of multiple sheets excel files.
We are always keen to meet the needs of users, whether it be bugs or issues found or positive changes you notice or improvements you’d like to see. You can contact us via this form to submit any queries you might have.
About the author
Allan Figueroa is a Software Developer, working in the Census Aggregate and International Macrodata team for the UK Data Service, which is based in Jisc. He works on the analysis and implementation of new features, as well as the ingesting of international data to our platforms.
